Ionization Energy:
Energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atomsFactors affecting Ionization Energy
Trend of ionization energy in the periodic table:
Ionization energy decreases down the group
- As we move down the group shell size increases and so the distance from the nucleus increases hence ionization energy decreases
- Also as we move down the group more electrons are being added, hence shielding affect increases.
- Ionization energy increases across the period
- As we move across the period the shielding affect remains constant
- BUT across the period atomic size decreases due to INCREASE in EFFECTIVE NUCLEAR CHARGE which causes the ionization energy to increase
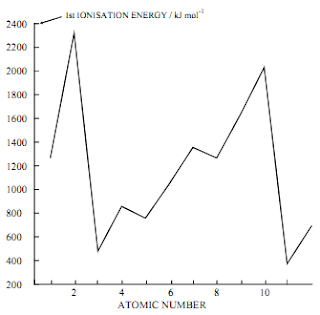
Ionisation Energy - Variation
He > H
One extra proton therefore the
nuclear charge is greater and the
extra electron has gone into the
same energy level. Increased
attraction makes the electron
harder to remove.
Li < He
Despite the increased nuclear
charge, the outer electron is held
less strongly because it is shielded
by full inner level of electrons and is
further away - easier to remove
Be > Li
Increased nuclear charge plus the
electrons in the same energy level
O < N
Despite the increased nuclear charge the electron is easier to remove. This is because,
in N the three electrons in the 2p level are in separate orbitals whereas in O two of the
four electrons are in the same orbital. This leads to repulsion so less energy is needed
for the removal of one of them.
Na < Li
Despite the increased nuclear charge due to the larger number of protons in the nucleus
the increased shielding due to filled inner energy levels coupled with the greater distance
from the nucleus means that the outer electron is held less strongly and easier to remove
ATOMIC NUMBER
He > H
One extra proton therefore the
nuclear charge is greater and the
extra electron has gone into the
same energy level. Increased
attraction makes the electron
harder to remove.
Li < He
Despite the increased nuclear
charge, the outer electron is held
less strongly because it is shielded
by full inner level of electrons and is
further away - easier to remove
Be > Li
Increased nuclear charge plus the
electrons in the same energy level
O < N
Despite the increased nuclear charge the electron is easier to remove. This is because,
in N the three electrons in the 2p level are in separate orbitals whereas in O two of the
four electrons are in the same orbital. This leads to repulsion so less energy is needed
for the removal of one of them.
Na < Li
Despite the increased nuclear charge due to the larger number of protons in the nucleus
the increased shielding due to filled inner energy levels coupled with the greater distance
from the nucleus means that the outer electron is held less strongly and easier to remove
ATOMIC NUMBER








0 comments:
Post a Comment